New Structure Seat Latch Series X

.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
|
Unlocking force |
10N~49N |
|
|
Locking force |
≤50N |
|
|
Static strength |
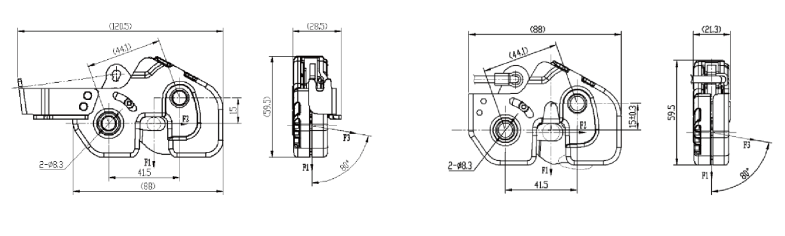
F1 |
25KN |
|
F2 |
10KN |
|
|
F3 |
10.5KN |
|
|
Durability |
≥7000 Cycle |
|
|
Fully unlocking trip |
16.9mm(33.8°) |
|
|
Single lock weight |
228g |
|
|
Unlock mode |
Lever |
|
|
Cable,Lever |
||
|
Tolerance |
±4mm/±3mm |
|
|
Adapter lock |
Φ8 |
|
|
Φ10 |
||
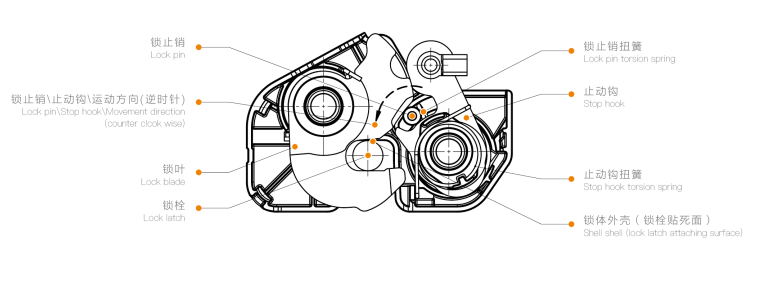
1.The lock ring impacts the lock leaf and snugly fits against the lock body shell.
2.The retaining hook and locking pin rotate towards the lock leaf under the action of the torsion spring. In the process, the retaining hook will rotate to its maximum position and then stop.
3.The key point for automatic gap compensation is the locking pin. After the locking pin meshes with the lock leaf, the movement force of the locking pin continues due to the action of the torsion spring. If the lock bolt does not snugly fit against the lock body shell, there will be a gap between the lock leaf, lock ring, and lock body shell (lock bolt snug fit face), which is the source of abnormal noise. The function of the locking pin is to eliminate this gap. If there is a gap (the lock bolt does not snugly fit against the lock body shell), the inertia generated by the vehicle’s bumps will cause the lock ring to momentarily snugly fit against the lock body shell. During this moment, the locking pin will move towards the lock leaf relying on the force of the torsion spring and get stuck between the lock leaf and the retaining hook.


.png?x-oss-process=image/resize)
.png)











































































.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)